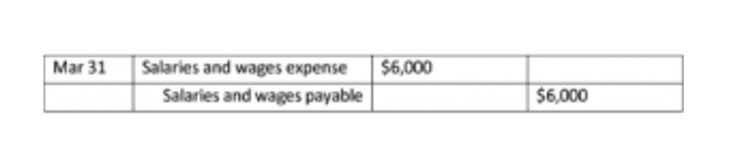
On the other hand, when an investor does not exercise full control or have significant influence over the investee, they would need to record their investment using the cost method. In this situation, the investment is recorded on the balance sheet at its historical cost. At the end of the year, ABC Company records a debit in the amount of $12,500 (25% of XYZ’s $50,000 net income) to “Investment in XYZ Corp”, and a credit in the same amount to Investment Revenue. Put another way, it is the amount that would remain if the company liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its debts. In other words, the total amount of all assets will always equal the sum of liabilities and shareholders’ equity. This number is the sum of total earnings that were not paid to shareholders as dividends.
- If an investor exercises neither control nor significant influence over the acquiree, the proper method of accounting for the investor is the fair value method.
- For example, if the investor directly appoints management in production, marketing, finance, and R&D departments, it can spread its control and reach across the investee company.
- In the above example, there is no goodwill, so net identifiable assets will be the difference between total assets and total liabilities, which is reflected in shareholders’ equity.
- The ability to exercise significant influence is often related to an investor’s ownership interest in the investee on the basis of common stock and in-substance common stock.
- To calculate the Realized Gain or Loss in each period, we need the Cost Basis right before the change takes place, as well as the market value at which the stake was sold.
- Equity accounting reflects a measurement approach as well as a consolidation approach.
Under the equity method the investor records their share of loss using the following journal entry. For example, if the investee makes a profit it increases in value and the investor reflects its share of the increase in the carrying value shown on its investment account. If the investee makes a loss it decreases in value and the investor reflects its share of the decrease in the carrying value shown on its investment account. Profit and loss from the investee increase the investment account by an amount proportionate to the investor’s shares in the investee. It is known as the “equity pick-up.” Dividends paid out by the investee are deducted from the account. The equity method is the standard technique used when one company, the investor, has a significant influence over another company, the investee.
What Is the Equity Method of Accounting?
Investors may sell (downstream transactions) or purchase (upstream transactions) assets to or from investees. ASC 323 requires that investors and investees engage in these activities as arm’s length transactions. Lion receives dividends of $15,000, which is 30% of $50,000 and records a reduction in their investment account. In other words, there is an outflow of cash from the investee, as reflected in the reduced investment account.
Respondents to the IASB exposure drafts are generally not in favour of introducing accounting policy options in IFRS. The cost method of accounting is used when an investor owns less than 20% of the investee, holding a minority interest. In this case, investments are recorded as an asset using their historical cost. While the equity method makes periodic value adjustments, these values won’t change over time with the cost method. The purpose of equity accounting is to ensure that the investor’s accounts accurately reflect the investee’s profit and loss.
Impact of Upstream and Downstream Sales With an Example
Over 1.8 million professionals use CFI to learn accounting, financial analysis, modeling and more. Start with a free account to explore 20+ always-free courses and hundreds of finance templates and cheat sheets. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting.
As a result, any profit or loss from the investment is recorded as profit or loss to the company itself. When the investee company pays a cash dividend, the value of its net assets decreases. Using the equity method, the investor company receiving the dividend records equity method of accounting an increase to its cash balance but, meanwhile, reports a decrease in the carrying value of its investment. Other financial activities that affect the value of the investee’s net assets should have the same impact on the value of the investor’s share of investment.
Reversal of impairment losses under IFRS and GAAP
Although the following is only a general guideline, an investor is deemed to have significant influence over an investee if it owns between 20% to 50% of the investee’s shares or voting rights. If, however, the investor has less than 20% of the investee’s shares but still has a significant influence in its operations, then the investor must still use the equity method and not the cost method. The IASB feels including this option in IAS 27 would not involve any additional procedures because the information can be obtained from the consolidated financial statements by applying IFRS 10 and IAS 28. The equity method evolved as a basis of reporting the performance of subsidiaries partly as it was seen as more appropriate than cost.

This November 2023 edition incorporates updated guidance and interpretations. Unlike with the consolidation method, in using the equity method there is no consolidation and elimination process. Instead, the investor will report its proportionate share of the investee’s equity as an investment https://www.bookstime.com/ (at cost). One company can invest in another at any amount, and it is not always considered an acquisition. It is considered an acquisition if a company buys most or all of another company’s shares (50% or more) because the investor has effectively gained control of the investment company.
The investor records the receipt of its share of dividend with the following bookkeeping journal entry. The first of the equity method journal entries to be recorded is the initial cost of the investment of 220,000. Entity A holds a 20% interest in Entity B and accounts for it using the equity method. In the year 20X0, Entity B sold an item of inventory to Entity A for $1m, which was carried at a cost of $0.7m in B’s books. During the year 20X1, Entity A sold this inventory to its client for $1.5 million.