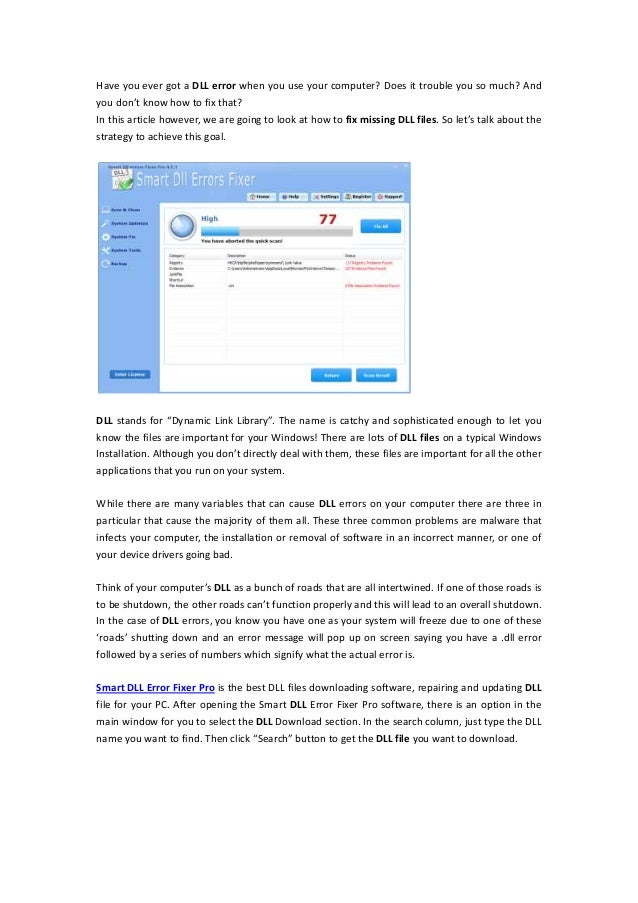
The main purpose of this tool is to view and change the settings in the system registry – a set of special files which contain configuration information about Windows and almost all software installed. Windows and many programs (except the ones which are "portable") use this information to read and write their own settings to the registry. Windows 9x/ME, Windows CE, Windows NT/2000/XP/2003 store configuration data in registry.
Windows Registry is nothing but a collection of different configurations and settings related to the operating system, programs, and users. You can think of it like a database that virtually stores all the important information.
In the Windows 98, CE, NT, and 2000 operating systems, a registry key is an organizational unit in the Windows registry, an internal database the computer uses to store configuration information. The registry in Windows stores data in binary format, keeping the configuration data for the machine and its users in separate files. This allows the system and its applications to load global and individual configurations upon startup and login. Registry Editor was born as a tool for users who want to change Windows settings which are not exposed in the user interface.
Due to the vast amount of information stored in Windows registry, the registry can be an excellent source for potential evidential data. For instance, windows registry contains information on user accounts, typed URLs, network shared, and Run command history. Aspects discussed in this paper are based solely on Windows XP (Service Pack 2) registry.
To improve performance or make Windows work the way you want, you can change registry key values manually using the Windows Registry Editor (regedit). Your registry files can also be changed by malware or due to errors during the installation of programs or drives; these unwanted changes are likely to degrade the performance of your computer or even damage it. .INI files stored each program’s user settings in a separate file. By contrast, the Windows registry stores all application settings in one central repository and in a standardized form.
Since accessing the registry does not require parsing, it may be read from or written to more quickly than an INI file. As well, strongly-typed data can be stored in the registry, as opposed to the text information stored in INI files. Many enterprise applications store their configuration information in the Windows registry, in local .XML files, or internal application-specific configuration stores. It is also important to understand how individual user accounts use the registry settings especially in a Terminal Services or Citrix environments. When configuring user-specific application settings saved in the Windows Registry, a Terminal Services environment could require logon and logoff scripts that import and export the registry settings.
- You can load these individually and mount them to the root of the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE key.
- Registry Editor also allows you to access the keys and values of another user on the same Windows installation or another Windows installation on a different or same PC.
- As mentioned above, the Windows Registry is stored in several files.
- Ever since Windows 95, the Windows operating system has been using a centralized hierarchical database to store system settings, hardware configurations, and user preferences.
- This database is called the Windows Registry or more commonly known as the Registry.
- The ease of use as well as the access to various customizations and settings in one central place has also made windows the preferred platform for desktop applications by various software developers.
Was The Windows Registry A Good Idea?
It is a central repository for msstdfmt.dll missing configuration data that is stored in a hierarchical manner. System, users, applications and hardware in Windows make use of the registry to store their configuration and it is constantly accessed for reference during their operation. The registry is introduced to replace most text-based configuration files used in Windows 3.x and MS-DOS, such as .ini files, autoexec.bat and config.sys.
What Is Windows Registry? [Minitool Wiki]
A hive in the registry is a group of keys, subkeys, and values in the registry that has a set of supporting files containing backups of its data. The Windows boot process automatically retrieves data from these supporting files.
This information includes anything related to system hardware, application settings, installed programs, user profiles, etc. I don’t believe any version of Windows we’ll see for the foreseeable future will throw out the registry for any new format, so making wishes is likely a wasted exercise.